7.1 KiB
enduser setup Module aka Captive Portal aka WiFi Manager
| Since | Origin / Contributor | Maintainer | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2015-09-02 | Robert Foss | Robert Foss | enduser_setup.c |
This module provides a simple way of configuring ESP8266 chips without using a serial interface or pre-programming WiFi credentials onto the chip.
After running enduser_setup.start(), a wireless
network named "NodeMCU_XXXXXX" will start. This prefix can be overridden
in user_config.h by defining ENDUSER_SETUP_AP_SSID or by supplying the whole SSID to the
enduser_setup.start method. Connect to that SSID and captive portal detection on the client
should automatically open the configuration dialog. If not, then
navigate to the root of any website or to 192.168.4.1.
http://example.com/ will work, but do not use .local domains because it
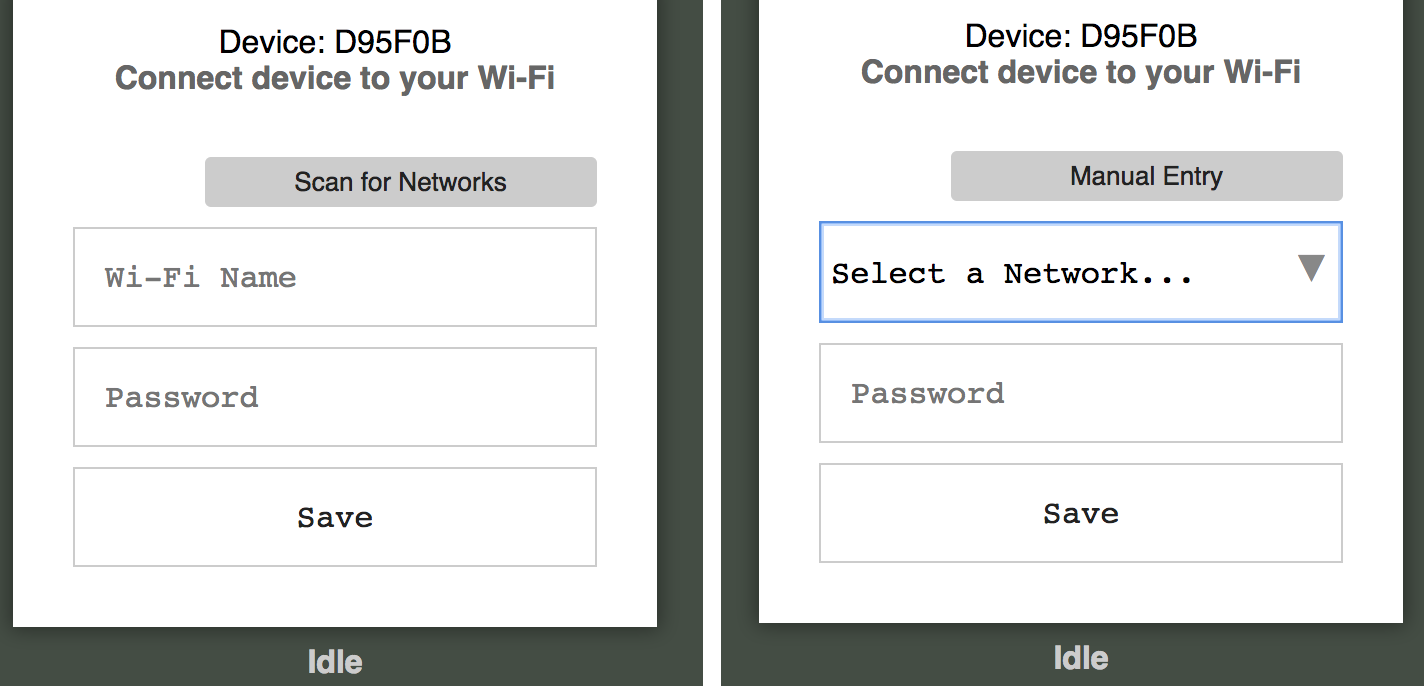
will fail on iOS. A web page similar to the one depicted below will load,
allowing the end user to provide their Wi-Fi credentials.
After an IP address has been successfully obtained, then this module will stop
as if enduser_setup.stop() had been called. There is a
10-second delay before teardown to allow connected clients to obtain a last
status message while the SoftAP is still active.
Alternative HTML can be served by placing a file called enduser_setup.html on
the filesystem. Everything needed by the web page must be included in this one
file. This file will be kept in RAM, so keep it as small as possible. The file
can be gzip'd ahead of time to reduce the size (i.e., using gzip -n or
zopfli), and when served, the End User Setup module will add the appropriate
Content-Encoding header to the response.
Note: If gzipped, the file can also be named enduser_setup.html.gz for
semantic purposes. GZIP encoding is determined by the file's contents, not the
filename.
Additional configuration parameters
You can also add some additional inputs in the enduser_setup.html (as long as
you keep those needed for the WiFi setup). The additional data will be written
in a eus_params.lua file in the root filesystem of the ESP8266, which you can
then load in your own code. In this case, the data will be saved as a set of
variables with the name being the input name, and the value being a string
representing what you put in the form.
For instance, if your HTML contains two additional inputs:
<input name=timeout_delay type=text placeholder="Delay in seconds" />
<input name=device_name type=text placeholder="Unique device name" />
Then the eus_params.lua file will contain the following:
-- those wifi_* are the base parameters that are saved anyway
-- if network is open, then there is no wifi_password
local p = {}
p.wifi_ssid="ssid"
p.wifi_password="password"
-- your own parameters:
p.timeout_delay="xxx"
p.device_name="yyy"
return p
How to use the eus_params.lua file
Simply include the file by using the dofile function:
p = dofile('eus_params.lua')
-- now use the parameters in the Lua table
print("Wifi device_name: " .. p.device_name)
HTTP endpoints:
| Path | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
| / | GET | Returns HTML for the web page. Will return the contents of enduser_setup.html if it exists on the filesystem, otherwise will return a page embedded into the firmware image. |
| /aplist | GET | Forces the ESP8266 to perform a site survey across all channels, reporting access points that it can find. Return payload is a JSON array: [{"ssid":"foobar","rssi":-36,"chan":3}] |
| /status | GET | Returns plaintext status description, used by the web page |
| /status.json | GET | Returns a JSON payload containing the ESP8266's chip id in hexadecimal format and the status code: 0=Idle, 1=Connecting, 2=Wrong Password, 3=Network not Found, 4=Failed, 5=Success |
| /setwifi | POST | HTML form post for setting the WiFi credentials. Expects HTTP content type application/x-www-form-urlencoded. Supports sending and storing additinal configuration parameters (as input fields). Returns the same payload as /status.json instead of redirecting to /. See also: /update. |
| /update | GET | Data submission target. Example: http://example.com/update?wifi_ssid=foobar&wifi_password=CorrectHorseBatteryStaple. Will redirect to / when complete. Note that will NOT update the eus_params.lua file i.e. it does NOT support sending arbitrary parameters. See also: /setwifi. |
Module functions are described below.
enduser_setup.manual()
Controls whether manual AP configuration is used.
By default the enduser_setup module automatically configures an open access
point when starting, and stops it when the device has been successfully joined
to a WiFi network. If manual mode has been enabled, neither of this is done.
The device must be manually configured for wifi.SOFTAP mode prior to calling
enduser_setup.start(). Additionally, the portal is not stopped after the
device has successfully joined to a WiFi network.
Syntax
enduser_setup.manual([on_off])
Parameters
on_offa boolean value indicating whether to use manual mode; if not given, the function only returns the current setting.
Returns
The current setting, true if manual mode is enabled, false if it is not.
Example
wifi.setmode(wifi.STATIONAP)
wifi.ap.config({ssid="MyPersonalSSID", auth=wifi.OPEN})
enduser_setup.manual(true)
enduser_setup.start(
function()
print("Connected to WiFi as:" .. wifi.sta.getip())
end,
function(err, str)
print("enduser_setup: Err #" .. err .. ": " .. str)
end
)
enduser_setup.start()
Starts the captive portal.
Note: Calling start() while EUS is already running is an error, and will result in stop() to be invoked to shut down EUS.
Syntax
enduser_setup.start([AP_SSID,] [onConnected()], [onError(err_num, string)], [onDebug(string)])
Parameters
AP_SSIDthe (optional) SSID to use for the AP. This defaults toNodeMCU_<device id>.onConnected()callback will be fired when an IP-address has been obtained, just before the enduser_setup module will terminate itselfonError()callback will be fired if an error is encountered.err_numis a number describing the error, andstringcontains a description of the error.onDebug()callback is disabled by default (controlled by#define ENDUSER_SETUP_DEBUG_ENABLEinenduser_setup.c). It is intended to be used to find internal issues in the module.stringcontains a description of what is going on.
Returns
nil
Example
enduser_setup.start(
function()
print("Connected to WiFi as:" .. wifi.sta.getip())
end,
function(err, str)
print("enduser_setup: Err #" .. err .. ": " .. str)
end,
print -- Lua print function can serve as the debug callback
)
enduser_setup.stop()
Stops the captive portal.
Syntax
enduser_setup.stop()
Parameters
none
Returns
nil