51 KiB
WiFi Module
| Since | Origin / Contributor | Maintainer | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2015-05-12 | Zeroday | dnc40085 | wifi.c |
!!! important The WiFi subsystem is maintained by background tasks that must run periodically. Any function or task that takes longer than 15ms (milliseconds) may cause the WiFi subsystem to crash. To avoid these potential crashes, it is advised that the WiFi subsystem be suspended with wifi.suspend() prior to the execution of any tasks or functions that exceed this 15ms guideline.
WiFi modes
Courtesy: content for this chapter is borrowed/inspired by the Arduino ESP8266 WiFi documentation.
Devices that connect to WiFi network are called stations (STA). Connection to Wi-Fi is provided by an access point (AP), that acts as a hub for one or more stations. The access point on the other end is connected to a wired network. An access point is usually integrated with a router to provide access from Wi-Fi network to the internet. Each access point is recognized by a SSID (Service Set IDentifier), that essentially is the name of network you select when connecting a device (station) to the WiFi.
Each ESP8266 module can operate as a station, so we can connect it to the WiFi network. It can also operate as a soft access point (soft-AP), to establish its own WiFi network. Therefore, we can connect other stations to such modules. Third, ESP8266 is also able to operate both in station and soft access point mode at the same time. This offers the possibility of building e.g. mesh networks.
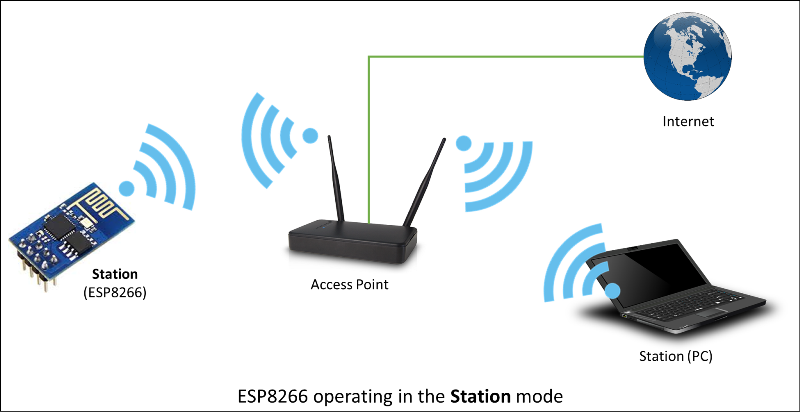
Station
Station (STA) mode is used to get the ESP8266 connected to a WiFi network established by an access point.
Soft Access Point
An access point (AP) is a device that provides access to Wi-Fi network to other devices (stations) and connects them further to a wired network. ESP8266 can provide similar functionality except it does not have interface to a wired network. Such mode of operation is called soft access point (soft-AP). The maximum number of stations connected to the soft-AP is five.
The soft-AP mode is often used and an intermediate step before connecting ESP to a WiFi in a station mode. This is when SSID and password to such network is not known upfront. The module first boots in soft-AP mode, so we can connect to it using a laptop or a mobile phone. Then we are able to provide credentials to the target network. Once done ESP is switched to the station mode and can connect to the target WiFi.
Such functionality is provided by the NodeMCU enduser setup module.
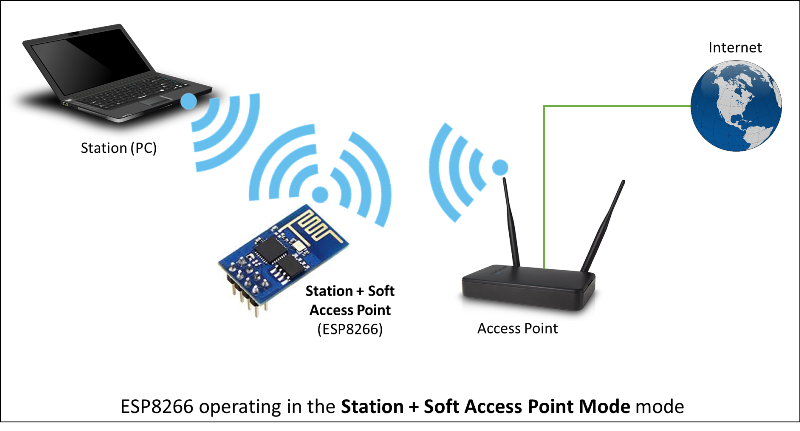
Station + Soft Access Point
Another handy application of soft-AP mode is to set up mesh networks. ESP can operate in both soft-AP and Station mode so it can act as a node of a mesh network.
Function reference
The NodeMCU WiFi control is spread across several tables:
wififor overall WiFi configurationwifi.stafor station mode functionswifi.apfor wireless access point (WAP or simply AP) functionswifi.ap.dhcpfor DHCP server controlwifi.eventmonfor wifi event monitorwifi.monitorfor wifi monitor mode
wifi.getchannel()
Gets the current WiFi channel.
Syntax
wifi.getchannel()
Parameters
nil
Returns
current WiFi channel
wifi.getcountry()
Get the current country info.
Syntax
wifi.getcountry()
Parameters
nil
Returns
country_infothis table contains the current country info configurationcountryCountry code, 2 character string.start_chStarting channel.end_chEnding channel.policyThe policy parameter determines which country info configuration to use, country info given to station by AP or local configuration.0Country policy is auto, NodeMCU will use the country info provided by AP that the station is connected to.1Country policy is manual, NodeMCU will use locally configured country info.
Example
for k, v in pairs(wifi.getcountry()) do
print(k, v)
end
See also
wifi.getdefaultmode()
Gets default WiFi operation mode.
Syntax
wifi.getdefaultmode()
Parameters
nil
Returns
The WiFi mode, as one of the wifi.STATION, wifi.SOFTAP, wifi.STATIONAP or wifi.NULLMODE constants.
See also
wifi.getmode()
Gets WiFi operation mode.
Syntax
wifi.getmode()
Parameters
nil
Returns
The WiFi mode, as one of the wifi.STATION, wifi.SOFTAP, wifi.STATIONAP or wifi.NULLMODE constants.
See also
wifi.getdefaultmode()
wifi.setmode()
wifi.getphymode()
Gets WiFi physical mode.
Syntax
wifi.getphymode()
Parameters
none
Returns
The current physical mode as one of wifi.PHYMODE_B, wifi.PHYMODE_G or wifi.PHYMODE_N.
See also
wifi.nullmodesleep()
Configures whether or not WiFi automatically goes to sleep in NULL_MODE. Enabled by default.
!!! note
This function does not store it's setting in flash, if auto sleep in NULL_MODE is not desired, wifi.nullmodesleep(false) must be called after power-up, restart, or wake from deep sleep.
Syntax
wifi.nullmodesleep([enable])
Parameters
enabletrueEnable WiFi auto sleep in NULL_MODE. (Default setting)falseDisable WiFi auto sleep in NULL_MODE.
Returns
sleep_enabledCurrent/New NULL_MODE sleep setting- If
wifi.nullmodesleep()is called with no arguments, current setting is returned. - If
wifi.nullmodesleep()is called withenableargument, confirmation of new setting is returned.
- If
wifi.resume()
Wake up WiFi from suspended state or cancel pending wifi suspension.
!!! attention
This is disabled by default. Modify PMSLEEP_ENABLE in app/include/user_config.h to enable it.
!!! note Wifi resume occurs asynchronously, this means that the resume request will only be processed when control of the processor is passed back to the SDK (after MyResumeFunction() has completed). The resume callback also executes asynchronously and will only execute after wifi has resumed normal operation.
Syntax
wifi.resume([resume_cb])
Parameters
-
resume_cbCallback to execute when WiFi wakes from suspension. !!! note "Note:"Any previously provided callbacks will be replaced!
Returns
nil
Example
--Resume wifi from timed or indefinite sleep
wifi.resume()
--Resume wifi from timed or indefinite sleep w/ resume callback
wifi.resume(function() print("WiFi resume") end)
See also
wifi.setcountry()
Set the current country info.
Syntax
wifi.setcountry(country_info)
Parameters
country_infoThis table contains the country info configuration. (If a blank table is passed to this function, default values will be configured.)countryCountry code, 2 character string containing the country code (a list of country codes can be found here). (Default:"CN")start_chStarting channel (range:1-14). (Default:1)end_chEnding channel, must not be less than starting channel (range:1-14). (Default:13)policyThe policy parameter determines which country info configuration to use, country info given to station by AP or local configuration. (default:wifi.COUNTRY_AUTO)wifi.COUNTRY_AUTOCountry policy is auto, NodeMCU will use the country info provided by AP that the station is connected to.- while in stationAP mode, beacon/probe respose will reflect the country info of the AP that the station is connected to.
wifi.COUNTRY_MANUALCountry policy is manual, NodeMCU will use locally configured country info.
Returns
true If configuration was sucessful.
Example
do
country_info={}
country_info.country="US"
country_info.start_ch=1
country_info.end_ch=13
country_info.policy=wifi.COUNTRY_AUTO;
wifi.setcountry(country_info)
end
--compact version
wifi.setcountry({country="US", start_ch=1, end_ch=13, policy=wifi.COUNTRY_AUTO})
--Set defaults
wifi.setcountry({})
See also
wifi.setmode()
Configures the WiFi mode to use. NodeMCU can run in one of four WiFi modes:
- Station mode, where the NodeMCU device joins an existing network
- Access point (AP) mode, where it creates its own network that others can join
- Station + AP mode, where it both creates its own network while at the same time being joined to another existing network
- WiFi off
When using the combined Station + AP mode, the same channel will be used for both networks as the radio can only listen on a single channel.
!!! note WiFi configuration will be retained until changed even if device is turned off.
Syntax
wifi.setmode(mode[, save])
Parameters
modevalue should be one ofwifi.STATIONfor when the device is connected to a WiFi router. This is often done to give the device access to the Internet.wifi.SOFTAPfor when the device is acting only as an access point. This will allow you to see the device in the list of WiFi networks (unless you hide the SSID, of course). In this mode your computer can connect to the device, creating a local area network. Unless you change the value, the NodeMCU device will be given a local IP address of 192.168.4.1 and assign your computer the next available IP address, such as 192.168.4.2.wifi.STATIONAPis the combination ofwifi.STATIONandwifi.SOFTAP. It allows you to create a local WiFi connection and connect to another WiFi router.wifi.NULLMODEchanging WiFi mode to NULL_MODE will put wifi into a low power state similar to MODEM_SLEEP, providedwifi.nullmodesleep(false)has not been called.
savechoose whether or not to save wifi mode to flashtrueWiFi mode configuration will be retained through power cycle. (Default)falseWiFi mode configuration will not be retained through power cycle.
Returns
current mode after setup
Example
wifi.setmode(wifi.STATION)
See also
wifi.getmode()
wifi.getdefaultmode()
wifi.setphymode()
Sets WiFi physical mode.
wifi.PHYMODE_B802.11b, more range, low Transfer rate, more current drawwifi.PHYMODE_G802.11g, medium range, medium transfer rate, medium current drawwifi.PHYMODE_N802.11n, least range, fast transfer rate, least current draw (STATION ONLY) Information from the Espressif datasheet v4.3
| Parameters | Typical Power Usage |
|---|---|
| Tx 802.11b, CCK 11Mbps, P OUT=+17dBm | 170 mA |
| Tx 802.11g, OFDM 54Mbps, P OUT =+15dBm | 140 mA |
| Tx 802.11n, MCS7 65Mbps, P OUT =+13dBm | 120 mA |
| Rx 802.11b, 1024 bytes packet length, -80dBm | 50 mA |
| Rx 802.11g, 1024 bytes packet length, -70dBm | 56 mA |
| Rx 802.11n, 1024 bytes packet length, -65dBm | 56 mA |
Syntax
wifi.setphymode(mode)
Parameters
mode one of the following
wifi.PHYMODE_Bwifi.PHYMODE_Gwifi.PHYMODE_N
Returns
physical mode after setup
See also
wifi.setmaxtxpower()
Sets WiFi maximum TX power. This setting is not persisted across power cycles, and the Espressif SDK documentation does not specify if the setting persists after deep sleep. The default value used is read from byte 34 of the ESP8266 init data, and its value is hence defined by the manufacturer.
The default value, 82, corresponds to maximum TX power. Lowering this setting could reduce power consumption on battery backed devices.
Syntax
wifi.setmaxtxpower(max_tpw)
Parameters
max_tpw maximum value of RF Tx Power, unit: 0.25 dBm, range [0, 82].
Returns
nil
See also
wifi.startsmart()
Starts to auto configuration, if success set up SSID and password automatically.
Intended for use with SmartConfig apps, such as Espressif's Android & iOS app.
Only usable in wifi.STATION mode.
!!! important
SmartConfig is disabled by default and can be enabled by setting `WIFI_SMART_ENABLE` in [`user_config.h`](https://github.com/nodemcu/nodemcu-firmware/blob/dev/app/include/user_config.h#L96) before you build the firmware.
Syntax
wifi.startsmart(type, callback)
Parameters
type0 for ESP_TOUCH, or 1 for AIR_KISS.callbacka callback function of the formfunction(ssid, password) endwhich gets called after configuration.
Returns
nil
Example
wifi.setmode(wifi.STATION)
wifi.startsmart(0,
function(ssid, password)
print(string.format("Success. SSID:%s ; PASSWORD:%s", ssid, password))
end
)
See also
wifi.stopsmart()
Stops the smart configuring process.
Syntax
wifi.stopsmart()
Parameters
none
Returns
nil
See also
wifi.suspend()
Suspend Wifi to reduce current consumption.
!!! attention
This is disabled by default. Modify PMSLEEP_ENABLE in app/include/user_config.h to enable it.
!!! note Wifi suspension occurs asynchronously, this means that the suspend request will only be processed when control of the processor is passed back to the SDK (after MySuspendFunction() has completed). The suspend callback also executes asynchronously and will only execute after wifi has been successfully been suspended.
Syntax
wifi.suspend({duration[, suspend_cb, resume_cb, preserve_mode]})
Parameters
durationSuspend duration in microseconds(μs). If a suspend duration of0is specified, suspension will be indefinite (Range: 0 or 50000 - 268435454 μs (0:4:28.000454))suspend_cbCallback to execute when WiFi is suspended. (Optional)resume_cbCallback to execute when WiFi wakes from suspension. (Optional)preserve_modepreserve current WiFi mode through node sleep. (Optional, Default: true)- If true, Station and StationAP modes will automatically reconnect to previously configured Access Point when NodeMCU resumes.
- If false, discard WiFi mode and leave NodeMCU in
wifi.NULL_MODE. WiFi mode will be restored to original mode on restart.
Returns
suspend_stateif no parameters are provided, current WiFi suspension state will be returned- States:
0WiFi is awake.1WiFi suspension is pending. (Waiting for idle task)2WiFi is suspended.
Example
--get current wifi suspension state
print(wifi.suspend())
--Suspend WiFi for 10 seconds with suspend/resume callbacks
cfg={}
cfg.duration=10*1000*1000
cfg.resume_cb=function() print("WiFi resume") end
cfg.suspend_cb=function() print("WiFi suspended") end
wifi.suspend(cfg)
--Suspend WiFi for 10 seconds with suspend/resume callbacks and discard WiFi mode
cfg={}
cfg.duration=10*1000*1000
cfg.resume_cb=function() print("WiFi resume") end
cfg.suspend_cb=function() print("WiFfi suspended") end
cfg.preserve_mode=false
wifi.suspend(cfg)
See also
wifi.sta Module
wifi.sta.autoconnect()
Auto connects to AP in station mode.
Syntax
wifi.sta.autoconnect(auto)
Parameters
auto 0 to disable auto connecting, 1 to enable auto connecting
Returns
nil
Example
wifi.sta.autoconnect(1)
See also
wifi.sta.changeap()
Select Access Point from list returned by wifi.sta.getapinfo()
Syntax
wifi.sta.changeap(ap_index)
Parameters
ap_index Index of Access Point you would like to change to. (Range:1-5)
- Corresponds to index used by
wifi.sta.getapinfo()andwifi.sta.getapindex()
Returns
trueSuccessfalseFailure
Example
wifi.sta.changeap(4)
See also
wifi.sta.clearconfig()
Clears the currently saved WiFi station configuration, erasing it from the flash. May be useful for certain factory-reset
scenarios when a full node.restore() is not desired, or to prepare for using
End-User Setup so that the SoftAP is able to lock onto a single hardware radio channel.
Syntax
wifi.sta.clearconfig()
Parameters
none
Returns
trueSuccessfalseFailure
See also
wifi.sta.config()
Sets the WiFi station configuration.
!!! note It is not advised to assume that the WiFi is connected at any time during initialization start-up. WiFi connection status should be validated either by using a WiFi event callback or by polling the status on a timer.
Syntax
wifi.sta.config(station_config)
Parameters
station_configtable containing configuration data for stationssidstring which is less than 32 bytes.pwdstring which is 0-64. Empty string indicates an open WiFi access point. Note: WPA requires a minimum of 8-characters, but the ESP8266 can also connect to a WEP access point (a 40-bit WEP key can be provided as its corresponding 5-character ASCII string).autodefaults to truetrueto enable auto connect and connect to access point, hence withauto=truethere's no need to callwifi.sta.connect()falseto disable auto connect and remain disconnected from access point
bssidstring that contains the MAC address of the access point (optional)- You can set BSSID if you have multiple access points with the same SSID.
- If you set BSSID for a specific SSID and would like to configure station to connect to the same SSID only without the BSSID requirement, you MUST first configure to station to a different SSID first, then connect to the desired SSID
- The following formats are valid:
- "DE:C1:A5:51:F1:ED"
- "AC-1D-1C-B1-0B-22"
- "DE AD BE EF 7A C0"
saveSave station configuration to flash.trueconfiguration will be retained through power cycle. (Default).falseconfiguration will not be retained through power cycle.
- Event callbacks will only be available if
WIFI_SDK_EVENT_MONITOR_ENABLEis uncommented inuser_config.h- Please note: To ensure all station events are handled at boot time, all relevant callbacks must be registered as early as possible in
init.luawith eitherwifi.sta.config()orwifi.eventmon.register(). connected_cb: Callback to execute when station is connected to an access point. (Optional)- Items returned in table :
SSID: SSID of access point. (format: string)BSSID: BSSID of access point. (format: string)channel: The channel the access point is on. (format: number)
- Items returned in table :
disconnected_cb: Callback to execute when station is disconnected from an access point. (Optional)- Items returned in table :
SSID: SSID of access point. (format: string)BSSID: BSSID of access point. (format: string)reason: See wifi.eventmon.reason below. (format: number)
- Items returned in table :
authmode_change_cb: Callback to execute when the access point has changed authorization mode. (Optional)- Items returned in table :
old_auth_mode: Old wifi authorization mode. (format: number)new_auth_mode: New wifi authorization mode. (format: number)
got_ip_cb: Callback to execute when the station received an IP address from the access point. (Optional)- Items returned in table :
IP: The IP address assigned to the station. (format: string)netmask: Subnet mask. (format: string)gateway: The IP address of the access point the station is connected to. (format: string)
- Items returned in table :
dhcp_timeout_cb: Station DHCP request has timed out. (Optional)- Blank table is returned.
- Please note: To ensure all station events are handled at boot time, all relevant callbacks must be registered as early as possible in
Returns
trueSuccessfalseFailure
Example
--connect to Access Point (DO NOT save config to flash)
station_cfg={}
station_cfg.ssid="NODE-AABBCC"
station_cfg.pwd="password"
station_cfg.save=false
wifi.sta.config(station_cfg)
--connect to Access Point (DO save config to flash)
station_cfg={}
station_cfg.ssid="NODE-AABBCC"
station_cfg.pwd="password"
station_cfg.save=true
wifi.sta.config(station_cfg)
--connect to Access Point with specific MAC address (DO save config to flash)
station_cfg={}
station_cfg.ssid="NODE-AABBCC"
station_cfg.pwd="password"
station_cfg.bssid="AA:BB:CC:DD:EE:FF"
wifi.sta.config(station_cfg)
--configure station but don't connect to Access point (DO save config to flash)
station_cfg={}
station_cfg.ssid="NODE-AABBCC"
station_cfg.pwd="password"
station_cfg.auto=false
wifi.sta.config(station_cfg)
See also
wifi.sta.connect()
Connects to the configured AP in station mode. You only ever need to call this if auto-connect was disabled in wifi.sta.config().
Syntax
wifi.sta.connect([connected_cb])
Parameters
connected_cb: Callback to execute when station is connected to an access point. (Optional)- Items returned in table :
SSID: SSID of access point. (format: string)BSSID: BSSID of access point. (format: string)channel: The channel the access point is on. (format: number)
- Items returned in table :
Returns
nil
See also
wifi.sta.disconnect()
Disconnects from AP in station mode.
!!! note
Please note that disconnecting from Access Point does not reduce power consumption. If power saving is your goal, please refer to the description for wifi.NULLMODE in the function wifi.setmode() for more details.
Syntax
wifi.sta.disconnect([disconnected_cb])
Parameters
disconnected_cb: Callback to execute when station is disconnected from an access point. (Optional)- Items returned in table :
SSID: SSID of access point. (format: string)BSSID: BSSID of access point. (format: string)reason: See wifi.eventmon.reason below. (format: number)
- Items returned in table :
Returns
nil
See also
wifi.sta.getap()
Scans AP list as a Lua table into callback function.
Syntax
wifi.sta.getap([[cfg], format,] callback(table))
Parameters
cfgtable that contains scan configurationssidSSID == nil, don't filter SSIDbssidBSSID == nil, don't filter BSSIDchannelchannel == 0, scan all channels, otherwise scan set channel (default is 0)show_hiddenshow_hidden == 1, get info for router with hidden SSID (default is 0)
formatselect output table format, defaults to 0- 0: old format (SSID : Authmode, RSSI, BSSID, Channel), any duplicate SSIDs will be discarded
- 1: new format (BSSID : SSID, RSSI, auth mode, Channel)
callback(table)a callback function to receive the AP table when the scan is done. This function receives a table, the key is the BSSID, the value is other info in format: SSID, RSSID, auth mode, channel.
Returns
nil
Example
-- print AP list in old format (format not defined)
function listap(t)
for k,v in pairs(t) do
print(k.." : "..v)
end
end
wifi.sta.getap(listap)
-- Print AP list that is easier to read
function listap(t) -- (SSID : Authmode, RSSI, BSSID, Channel)
print("\n"..string.format("%32s","SSID").."\tBSSID\t\t\t\t RSSI\t\tAUTHMODE\tCHANNEL")
for ssid,v in pairs(t) do
local authmode, rssi, bssid, channel = string.match(v, "([^,]+),([^,]+),([^,]+),([^,]+)")
print(string.format("%32s",ssid).."\t"..bssid.."\t "..rssi.."\t\t"..authmode.."\t\t\t"..channel)
end
end
wifi.sta.getap(listap)
-- print AP list in new format
function listap(t)
for k,v in pairs(t) do
print(k.." : "..v)
end
end
wifi.sta.getap(1, listap)
-- Print AP list that is easier to read
function listap(t) -- (SSID : Authmode, RSSI, BSSID, Channel)
print("\n\t\t\tSSID\t\t\t\t\tBSSID\t\t\t RSSI\t\tAUTHMODE\t\tCHANNEL")
for bssid,v in pairs(t) do
local ssid, rssi, authmode, channel = string.match(v, "([^,]+),([^,]+),([^,]+),([^,]*)")
print(string.format("%32s",ssid).."\t"..bssid.."\t "..rssi.."\t\t"..authmode.."\t\t\t"..channel)
end
end
wifi.sta.getap(1, listap)
--check for specific AP
function listap(t)
print("\n\t\t\tSSID\t\t\t\t\tBSSID\t\t\t RSSI\t\tAUTHMODE\t\tCHANNEL")
for bssid,v in pairs(t) do
local ssid, rssi, authmode, channel = string.match(v, "([^,]+),([^,]+),([^,]+),([^,]*)")
print(string.format("%32s",ssid).."\t"..bssid.."\t "..rssi.."\t\t"..authmode.."\t\t\t"..channel)
end
end
scan_cfg = {}
scan_cfg.ssid = "myssid"
scan_cfg.bssid = "AA:AA:AA:AA:AA:AA"
scan_cfg.channel = 0
scan_cfg.show_hidden = 1
wifi.sta.getap(scan_cfg, 1, listap)
--get RSSI for currently configured AP
function listap(t)
for bssid,v in pairs(t) do
local ssid, rssi, authmode, channel = string.match(v, "([^,]+),([^,]+),([^,]+),([^,]*)")
print("CURRENT RSSI IS: "..rssi)
end
end
ssid, tmp, bssid_set, bssid=wifi.sta.getconfig()
scan_cfg = {}
scan_cfg.ssid = ssid
if bssid_set == 1 then scan_cfg.bssid = bssid else scan_cfg.bssid = nil end
scan_cfg.channel = wifi.getchannel()
scan_cfg.show_hidden = 0
ssid, tmp, bssid_set, bssid=nil, nil, nil, nil
wifi.sta.getap(scan_cfg, 1, listap)
See also
wifi.sta.getapindex()
Get index of current Access Point stored in AP cache.
Syntax
wifi.sta.getapindex()
Parameters
none
Returns
current_index index of currently selected Access Point. (Range:1-5)
Example
print("the index of the currently selected AP is: "..wifi.sta.getapindex())
See also
wifi.sta.getapinfo()
Get information of APs cached by ESP8266 station.
!!! Note
Any Access Points configured with save disabled wifi.sta.config({save=false}) will populate this list (appearing to overwrite APs stored in flash) until restart.
Syntax
wifi.sta.getapinfo()
Parameters
nil
Returns
ap_infoqtyquantity of APs returned1-5index of AP. (the index corresponds to index used bywifi.sta.changeap()andwifi.sta.getapindex())ssidssid of Access Pointpwdpassword for Access Point,nilif no password was configuredbssidMAC address of Access Pointnilwill be returned if no MAC address was configured during station configuration.
Example
--print stored access point info
do
for k,v in pairs(wifi.sta.getapinfo()) do
if (type(v)=="table") then
print(" "..k.." : "..type(v))
for k,v in pairs(v) do
print("\t\t"..k.." : "..v)
end
else
print(" "..k.." : "..v)
end
end
end
--print stored access point info(formatted)
do
local x=wifi.sta.getapinfo()
local y=wifi.sta.getapindex()
print("\n Number of APs stored in flash:", x.qty)
print(string.format(" %-6s %-32s %-64s %-18s", "index:", "SSID:", "Password:", "BSSID:"))
for i=1, (x.qty), 1 do
print(string.format(" %s%-6d %-32s %-64s %-18s",(i==y and ">" or " "), i, x[i].ssid, x[i].pwd and x[i].pwd or type(nil), x[i].bssid and x[i].bssid or type(nil)))
end
end
See also
wifi.sta.getbroadcast()
Gets the broadcast address in station mode.
Syntax
wifi.sta.getbroadcast()
Parameters
nil
Returns
broadcast address as string, for example "192.168.0.255",
returns nil if IP address = "0.0.0.0".
See also
wifi.sta.getconfig()
Gets the WiFi station configuration.
Syntax
wifi.sta.getconfig()
Parameters
return_tabletruereturns data in a tablefalsereturns data in the old format (default)
Returns
If return_table is true:
config_tablessidssid of Access Point.pwdpassword to Access Point,nilif no password was configuredbssid_setwill returntrueif the station was configured specifically to connect to the AP with the matchingbssid.bssidIf a connection has been made to the configured AP this field will contain the AP's MAC address. Otherwise "ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff" will be returned.
If return_table is false:
- ssid, password, bssid_set, bssid, if
bssid_setis equal to0thenbssidis irrelevant
Example
--Get current Station configuration (NEW FORMAT)
do
local sta_config=wifi.sta.getconfig(true)
print(string.format("\tCurrent station config\n\tssid:\"%s\"\tpassword:\"%s\"\n\tbssid:\"%s\"\tbssid_set:%s", sta_config.ssid, sta_config.pwd, sta_config.bssid, (sta_config.bssid_set and "true" or "false")))
end
--Get current Station configuration (OLD FORMAT)
ssid, password, bssid_set, bssid=wifi.sta.getconfig()
print("\nCurrent Station configuration:\nSSID : "..ssid
.."\nPassword : "..password
.."\nBSSID_set : "..bssid_set
.."\nBSSID: "..bssid.."\n")
ssid, password, bssid_set, bssid=nil, nil, nil, nil
See also
wifi.sta.getdefaultconfig()
Gets the default WiFi station configuration stored in flash.
Syntax
wifi.sta.getdefaultconfig(return_table)
Parameters
return_tabletruereturns data in a tablefalsereturns data in the old format (default)
Returns
If return_table is true:
config_tablessidssid of Access Point.pwdpassword to Access Point,nilif no password was configuredbssid_setwill returntrueif the station was configured specifically to connect to the AP with the matchingbssid.bssidIf a connection has been made to the configured AP this field will contain the AP's MAC address. Otherwise "ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff" will be returned.
If return_table is false:
- ssid, password, bssid_set, bssid, if
bssid_setis equal to0thenbssidis irrelevant
Example
--Get default Station configuration (NEW FORMAT)
do
local def_sta_config=wifi.sta.getdefaultconfig(true)
print(string.format("\tDefault station config\n\tssid:\"%s\"\tpassword:\"%s\"\n\tbssid:\"%s\"\tbssid_set:%s", def_sta_config.ssid, def_sta_config.pwd, def_sta_config.bssid, (def_sta_config.bssid_set and "true" or "false")))
end
--Get default Station configuration (OLD FORMAT)
ssid, password, bssid_set, bssid=wifi.sta.getdefaultconfig()
print("\nCurrent Station configuration:\nSSID : "..ssid
.."\nPassword : "..password
.."\nBSSID_set : "..bssid_set
.."\nBSSID: "..bssid.."\n")
ssid, password, bssid_set, bssid=nil, nil, nil, nil
See also
wifi.sta.gethostname()
Gets current station hostname.
Syntax
wifi.sta.gethostname()
Parameters
none
Returns
currently configured hostname
Example
print("Current hostname is: \""..wifi.sta.gethostname().."\"")
wifi.sta.getip()
Gets IP address, netmask, and gateway address in station mode.
Syntax
wifi.sta.getip()
Parameters
none
Returns
IP address, netmask, gateway address as string, for example "192.168.0.111". Returns nil if IP = "0.0.0.0".
Example
-- print current IP address, netmask, gateway
print(wifi.sta.getip())
-- 192.168.0.111 255.255.255.0 192.168.0.1
ip = wifi.sta.getip()
print(ip)
-- 192.168.0.111
ip, nm = wifi.sta.getip()
print(nm)
-- 255.255.255.0
See also
wifi.sta.getmac()
Gets MAC address in station mode.
Syntax
wifi.sta.getmac()
Parameters
none
Returns
MAC address as string e.g. "18:fe:34:a2:d7:34"
See also
wifi.sta.getrssi()
Get RSSI(Received Signal Strength Indicator) of the Access Point which ESP8266 station connected to.
Syntax
wifi.sta.getrssi()
Parameters
none
Returns
- If station is connected to an access point,
rssiis returned. - If station is not connected to an access point,
nilis returned.
Example
RSSI=wifi.sta.getrssi()
print("RSSI is", RSSI)
wifi.sta.setaplimit()
Set Maximum number of Access Points to store in flash.
- This value is written to flash
!!! Attention New setting will not take effect until restart.
!!! Note
If 5 Access Points are stored and AP limit is set to 4, the AP at index 5 will remain until node.restore() is called or AP limit is set to 5 and AP is overwritten.
Syntax
wifi.sta.setaplimit(qty)
Parameters
qty Quantity of Access Points to store in flash. Range: 1-5 (Default: 1)
Returns
trueSuccessfalseFailure
Example
wifi.sta.setaplimit(5)
See also
wifi.sta.sethostname()
Sets station hostname.
Syntax
wifi.sta.sethostname(hostname)
Parameters
hostname must only contain letters, numbers and hyphens('-') and be 32 characters or less with first and last character being alphanumeric
Returns
trueSuccessfalseFailure
Example
if (wifi.sta.sethostname("NodeMCU") == true) then
print("hostname was successfully changed")
else
print("hostname was not changed")
end
wifi.sta.setip()
Sets IP address, netmask, gateway address in station mode.
Syntax
wifi.sta.setip(cfg)
Parameters
cfg table contain IP address, netmask, and gateway
{
ip = "192.168.0.111",
netmask = "255.255.255.0",
gateway = "192.168.0.1"
}
Returns
true if success, false otherwise
See also
wifi.sta.setmac()
Sets MAC address in station mode.
Syntax
wifi.sta.setmac(mac)
Parameters
MAC address in string e.g. "DE:AD:BE:EF:7A:C0"
Returns
true if success, false otherwise
Example
print(wifi.sta.setmac("DE:AD:BE:EF:7A:C0"))
See also
wifi.sta.sleeptype()
Configures the WiFi modem sleep type to be used while station is connected to an Access Point.
!!! note
Does not apply to wifi.SOFTAP, wifi.STATIONAP or wifi.NULLMODE.
Syntax
wifi.sta.sleeptype(type_wanted)
Parameters
type_wanted one of the following:
wifi.NONE_SLEEPto keep the modem on at all timeswifi.LIGHT_SLEEPto allow the CPU to power down under some circumstanceswifi.MODEM_SLEEPto power down the modem as much as possible
Returns
The actual sleep mode set, as one of wifi.NONE_SLEEP, wifi.LIGHT_SLEEP or wifi.MODEM_SLEEP.
wifi.sta.status()
Gets the current status in station mode.
Syntax
wifi.sta.status()
Parameters
nil
Returns
The current state which can be one of the following:
wifi.STA_IDLEwifi.STA_CONNECTINGwifi.STA_WRONGPWDwifi.STA_APNOTFOUNDwifi.STA_FAILwifi.STA_GOTIP
wifi.ap Module
wifi.ap.config()
Sets SSID and password in AP mode. Be sure to make the password at least 8 characters long! If you don't it will default to no password and not set the SSID! It will still work as an access point but use a default SSID like e.g. NODE_9997C3.
Syntax
wifi.ap.config(cfg)
Parameters
cfgtable to hold configurationssidSSID chars 1-32pwdpassword chars 8-64authauthentication method, one ofwifi.OPEN(default),wifi.WPA_PSK,wifi.WPA2_PSK,wifi.WPA_WPA2_PSKchannelchannel number 1-14 default = 6hiddenfalse = not hidden, true = hidden, default = falsemaxmaximum number of connections 1-4 default=4beaconbeacon interval time in range 100-60000, default = 100savesave configuration to flash.trueconfiguration will be retained through power cycle. (Default)falseconfiguration will not be retained through power cycle.
- Event callbacks will only be available if
WIFI_SDK_EVENT_MONITOR_ENABLEis uncommented inuser_config.h- Please note: To ensure all SoftAP events are handled at boot time, all relevant callbacks must be registered as early as possible in
init.luawith eitherwifi.ap.config()orwifi.eventmon.register(). staconnected_cb: Callback executed when a new client has connected to the access point. (Optional)- Items returned in table :
MAC: MAC address of client that has connected.AID: SDK provides no details concerning this return value.
- Items returned in table :
stadisconnected_cb: Callback executed when a client has disconnected from the access point. (Optional)- Items returned in table :
MAC: MAC address of client that has disconnected.AID: SDK provides no details concerning this return value.
- Items returned in table :
probereq_cb: Callback executed when a probe request was received. (Optional)- Items returned in table :
MAC: MAC address of the client that is probing the access point.RSSI: Received Signal Strength Indicator of client.
- Items returned in table :
- Please note: To ensure all SoftAP events are handled at boot time, all relevant callbacks must be registered as early as possible in
Returns
trueSuccessfalseFailure
Example:
cfg={}
cfg.ssid="myssid"
cfg.pwd="mypassword"
wifi.ap.config(cfg)
wifi.ap.deauth()
Deauths (forcibly removes) a client from the ESP access point by sending a corresponding IEEE802.11 management packet (first) and removing the client from it's data structures (afterwards).
The IEEE802.11 reason code used is 2 for "Previous authentication no longer valid"(AUTH_EXPIRE).
Syntax
wifi.ap.deauth([MAC])
Parameters
MACaddress of station to be deauthed.- Note: if this field is left blank, all currently connected stations will get deauthed.
Returns
Returns true unless called while the ESP is in the STATION opmode
Example
allowed_mac_list={"18:fe:34:00:00:00", "18:fe:34:00:00:01"}
wifi.eventmon.register(wifi.eventmon.AP_STACONNECTED, function(T)
print("\n\tAP - STATION CONNECTED".."\n\tMAC: "..T.MAC.."\n\tAID: "..T.AID)
if(allowed_mac_list~=nil) then
for _, v in pairs(allowed_mac_list) do
if(v == T.MAC) then return end
end
end
wifi.ap.deauth(T.MAC)
print("\tStation DeAuthed!")
end)
See also
wifi.eventmon.register()
wifi.eventmon.reason()
wifi.ap.getbroadcast()
Gets broadcast address in AP mode.
Syntax
wifi.ap.getbroadcast()
Parameters
none
Returns
broadcast address in string, for example "192.168.0.255",
returns nil if IP address = "0.0.0.0".
Example
bc = wifi.ap.getbroadcast()
print(bc)
-- 192.168.0.255
See also
wifi.ap.getclient()
Gets table of clients connected to device in AP mode.
Syntax
wifi.ap.getclient()
Parameters
none
Returns
table of connected clients
Example
table={}
table=wifi.ap.getclient()
for mac,ip in pairs(table) do
print(mac,ip)
end
-- or shorter
for mac,ip in pairs(wifi.ap.getclient()) do
print(mac,ip)
end
wifi.ap.getconfig()
Gets the current SoftAP configuration.
Syntax
wifi.ap.getconfig(return_table)
Parameters
return_tabletruereturns data in a tablefalsereturns data in the old format (default)
Returns
If return_table is true:
config_tablessidNetwork namepwdPassword,nilif no password was configured -authAuthentication Method (wifi.OPEN,wifi.WPA_PSK,wifi.WPA2_PSKorwifi.WPA_WPA2_PSK)channelChannel numberhiddenfalse= not hidden,true= hiddenmaxMaximum number of client connectionsbeaconBeacon interval
If return_table is false:
- ssid, password, if
bssid_setis equal to 0 thenbssidis irrelevant
Example
--Get SoftAP configuration table (NEW FORMAT)
do
print("\n Current SoftAP configuration:")
for k,v in pairs(wifi.ap.getconfig(true)) do
print(" "..k.." :",v)
end
end
--Get current SoftAP configuration (OLD FORMAT)
do
local ssid, password=wifi.ap.getconfig()
print("\n Current SoftAP configuration:\n SSID : "..ssid..
"\n Password :",password)
ssid, password=nil, nil
end
wifi.ap.getdefaultconfig()
Gets the default SoftAP configuration stored in flash.
Syntax
wifi.ap.getdefaultconfig(return_table)
Parameters
return_tabletruereturns data in a tablefalsereturns data in the old format (default)
Returns
If return_table is true:
config_tablessidNetwork namepwdPassword,nilif no password was configured -authAuthentication Method (wifi.OPEN,wifi.WPA_PSK,wifi.WPA2_PSKorwifi.WPA_WPA2_PSK)channelChannel numberhiddenfalse= not hidden,true= hiddenmaxMaximum number of client connectionsbeaconBeacon interval
If return_table is false:
- ssid, password, if
bssid_setis equal to 0 thenbssidis irrelevant
Example
--Get default SoftAP configuration table (NEW FORMAT)
do
print("\n Default SoftAP configuration:")
for k,v in pairs(wifi.ap.getdefaultconfig(true)) do
print(" "..k.." :",v)
end
end
--Get default SoftAP configuration (OLD FORMAT)
do
local ssid, password=wifi.ap.getdefaultconfig()
print("\n Default SoftAP configuration:\n SSID : "..ssid..
"\n Password :",password)
ssid, password=nil, nil
end
wifi.ap.getip()
Gets IP address, netmask and gateway in AP mode.
Syntax
wifi.ap.getip()
Parameters
none
Returns
IP address, netmask, gateway address as string, for example "192.168.0.111", returns nil if IP address = "0.0.0.0".
Example
-- print current ip, netmask, gateway
print(wifi.ap.getip())
-- 192.168.4.1 255.255.255.0 192.168.4.1
ip = wifi.ap.getip()
print(ip)
-- 192.168.4.1
ip, nm = wifi.ap.getip()
print(nm)
-- 255.255.255.0
ip, nm, gw = wifi.ap.getip()
print(gw)
-- 192.168.4.1
See also
wifi.ap.getmac()
Gets MAC address in AP mode.
Syntax
wifi.ap.getmac()
Parameters
none
Returns
MAC address as string, for example "1A-33-44-FE-55-BB"
See also
wifi.ap.setip()
Sets IP address, netmask and gateway address in AP mode.
Syntax
wifi.ap.setip(cfg)
Parameters
cfg table contain IP address, netmask, and gateway
Returns
true if successful, false otherwise
Example
cfg =
{
ip="192.168.1.1",
netmask="255.255.255.0",
gateway="192.168.1.1"
}
wifi.ap.setip(cfg)
See also
wifi.ap.setmac()
Sets MAC address in AP mode.
Syntax
wifi.ap.setmac(mac)
Parameters
MAC address in byte string, for example "AC-1D-1C-B1-0B-22"
Returns
true if success, false otherwise
Example
print(wifi.ap.setmac("AC-1D-1C-B1-0B-22"))
See also
wifi.ap.dhcp Module
wifi.ap.dhcp.config()
Configure the dhcp service. Currently only supports setting the start address of the dhcp address pool.
Syntax
wifi.ap.dhcp.config(dhcp_config)
Parameters
dhcp_config table containing the start-IP of the DHCP address pool, eg. "192.168.1.100"
Returns
pool_startip, pool_endip
Example
dhcp_config ={}
dhcp_config.start = "192.168.1.100"
wifi.ap.dhcp.config(dhcp_config)
wifi.ap.dhcp.start()
Starts the DHCP service.
Syntax
wifi.ap.dhcp.start()
Parameters
none
Returns
boolean indicating success
wifi.ap.dhcp.stop()
Stops the DHCP service.
Syntax
wifi.ap.dhcp.stop()
Parameters
none
Returns
boolean indicating success
wifi.eventmon Module
wifi.eventmon.register()
Register/unregister callbacks for WiFi event monitor.
- After a callback is registered, this function may be called to update a callback's function at any time
!!! note
To ensure all WiFi events are caught, the Wifi event monitor callbacks should be registered as early as possible in init.lua. Any events that occur before callbacks are registered will be discarded!
Syntax
wifi.eventmon.register(Event[, function(T)])
Parameters
Event: WiFi event you would like to set a callback for.
- Valid WiFi events:
- wifi.eventmon.STA_CONNECTED
- wifi.eventmon.STA_DISCONNECTED
- wifi.eventmon.STA_AUTHMODE_CHANGE
- wifi.eventmon.STA_GOT_IP
- wifi.eventmon.STA_DHCP_TIMEOUT
- wifi.eventmon.AP_STACONNECTED
- wifi.eventmon.AP_STADISCONNECTED
- wifi.eventmon.AP_PROBEREQRECVED
Returns
Function:
nil
Callback: T: Table returned by event.
wifi.eventmon.STA_CONNECTEDStation is connected to access point.SSID: SSID of access point.BSSID: BSSID of access point.channel: The channel the access point is on.
wifi.eventmon.STA_DISCONNECTED: Station was disconnected from access point.SSID: SSID of access point.BSSID: BSSID of access point.reason: See wifi.eventmon.reason below.
wifi.eventmon.STA_AUTHMODE_CHANGE: Access point has changed authorization mode.old_auth_mode: Old wifi authorization mode.new_auth_mode: New wifi authorization mode.
wifi.eventmon.STA_GOT_IP: Station got an IP address.IP: The IP address assigned to the station.netmask: Subnet mask.gateway: The IP address of the access point the station is connected to.
wifi.eventmon.STA_DHCP_TIMEOUT: Station DHCP request has timed out.- Blank table is returned.
wifi.eventmon.AP_STACONNECTED: A new client has connected to the access point.MAC: MAC address of client that has connected.AID: SDK provides no details concerning this return value.
wifi.eventmon.AP_STADISCONNECTED: A client has disconnected from the access point.MAC: MAC address of client that has disconnected.AID: SDK provides no details concerning this return value.
wifi.eventmon.AP_PROBEREQRECVED: A probe request was received.MAC: MAC address of the client that is probing the access point.RSSI: Received Signal Strength Indicator of client.
wifi.eventmon.WIFI_MODE_CHANGE: WiFi mode has changed.old_auth_mode: Old WiFi mode.new_auth_mode: New WiFi mode.
Example
wifi.eventmon.register(wifi.eventmon.STA_CONNECTED, function(T)
print("\n\tSTA - CONNECTED".."\n\tSSID: "..T.SSID.."\n\tBSSID: "..
T.BSSID.."\n\tChannel: "..T.channel)
end)
wifi.eventmon.register(wifi.eventmon.STA_DISCONNECTED, function(T)
print("\n\tSTA - DISCONNECTED".."\n\tSSID: "..T.SSID.."\n\tBSSID: "..
T.BSSID.."\n\treason: "..T.reason)
end)
wifi.eventmon.register(wifi.eventmon.STA_AUTHMODE_CHANGE, function(T)
print("\n\tSTA - AUTHMODE CHANGE".."\n\told_auth_mode: "..
T.old_auth_mode.."\n\tnew_auth_mode: "..T.new_auth_mode)
end)
wifi.eventmon.register(wifi.eventmon.STA_GOT_IP, function(T)
print("\n\tSTA - GOT IP".."\n\tStation IP: "..T.IP.."\n\tSubnet mask: "..
T.netmask.."\n\tGateway IP: "..T.gateway)
end)
wifi.eventmon.register(wifi.eventmon.STA_DHCP_TIMEOUT, function()
print("\n\tSTA - DHCP TIMEOUT")
end)
wifi.eventmon.register(wifi.eventmon.AP_STACONNECTED, function(T)
print("\n\tAP - STATION CONNECTED".."\n\tMAC: "..T.MAC.."\n\tAID: "..T.AID)
end)
wifi.eventmon.register(wifi.eventmon.AP_STADISCONNECTED, function(T)
print("\n\tAP - STATION DISCONNECTED".."\n\tMAC: "..T.MAC.."\n\tAID: "..T.AID)
end)
wifi.eventmon.register(wifi.eventmon.AP_PROBEREQRECVED, function(T)
print("\n\tAP - PROBE REQUEST RECEIVED".."\n\tMAC: ".. T.MAC.."\n\tRSSI: "..T.RSSI)
end)
wifi.eventmon.register(wifi.eventmon.WIFI_MODE_CHANGED, function(T)
print("\n\tSTA - WIFI MODE CHANGED".."\n\told_mode: "..
T.old_mode.."\n\tnew_mode: "..T.new_mode)
end)
See also
wifi.eventmon.unregister()
Unregister callbacks for WiFi event monitor.
Syntax
wifi.eventmon.unregister(Event)
Parameters
Event: WiFi event you would like to set a callback for.
- Valid WiFi events:
- wifi.eventmon.STA_CONNECTED
- wifi.eventmon.STA_DISCONNECTED
- wifi.eventmon.STA_AUTHMODE_CHANGE
- wifi.eventmon.STA_GOT_IP
- wifi.eventmon.STA_DHCP_TIMEOUT
- wifi.eventmon.AP_STACONNECTED
- wifi.eventmon.AP_STADISCONNECTED
- wifi.eventmon.AP_PROBEREQRECVED
- wifi.eventmon.WIFI_MODE_CHANGED
Returns
nil
Example
wifi.eventmon.unregister(wifi.eventmon.STA_CONNECTED)
See also
wifi.eventmon.reason
Table containing disconnect reasons.
| Disconnect reason | value |
|---|---|
| wifi.eventmon.reason.UNSPECIFIED | 1 |
| wifi.eventmon.reason.AUTH_EXPIRE | 2 |
| wifi.eventmon.reason.AUTH_LEAVE | 3 |
| wifi.eventmon.reason.ASSOC_EXPIRE | 4 |
| wifi.eventmon.reason.ASSOC_TOOMANY | 5 |
| wifi.eventmon.reason.NOT_AUTHED | 6 |
| wifi.eventmon.reason.NOT_ASSOCED | 7 |
| wifi.eventmon.reason.ASSOC_LEAVE | 8 |
| wifi.eventmon.reason.ASSOC_NOT_AUTHED | 9 |
| wifi.eventmon.reason.DISASSOC_PWRCAP_BAD | 10 |
| wifi.eventmon.reason.DISASSOC_SUPCHAN_BAD | 11 |
| wifi.eventmon.reason.IE_INVALID | 13 |
| wifi.eventmon.reason.MIC_FAILURE | 14 |
| wifi.eventmon.reason.4WAY_HANDSHAKE_TIMEOUT | 15 |
| wifi.eventmon.reason.GROUP_KEY_UPDATE_TIMEOUT | 16 |
| wifi.eventmon.reason.IE_IN_4WAY_DIFFERS | 17 |
| wifi.eventmon.reason.GROUP_CIPHER_INVALID | 18 |
| wifi.eventmon.reason.PAIRWISE_CIPHER_INVALID | 19 |
| wifi.eventmon.reason.AKMP_INVALID | 20 |
| wifi.eventmon.reason.UNSUPP_RSN_IE_VERSION | 21 |
| wifi.eventmon.reason.INVALID_RSN_IE_CAP | 22 |
| wifi.eventmon.reason.802_1X_AUTH_FAILED | 23 |
| wifi.eventmon.reason.CIPHER_SUITE_REJECTED | 24 |
| wifi.eventmon.reason.BEACON_TIMEOUT | 200 |
| wifi.eventmon.reason.NO_AP_FOUND | 201 |
| wifi.eventmon.reason.AUTH_FAIL | 202 |
| wifi.eventmon.reason.ASSOC_FAIL | 203 |
| wifi.eventmon.reason.HANDSHAKE_TIMEOUT | 204 |